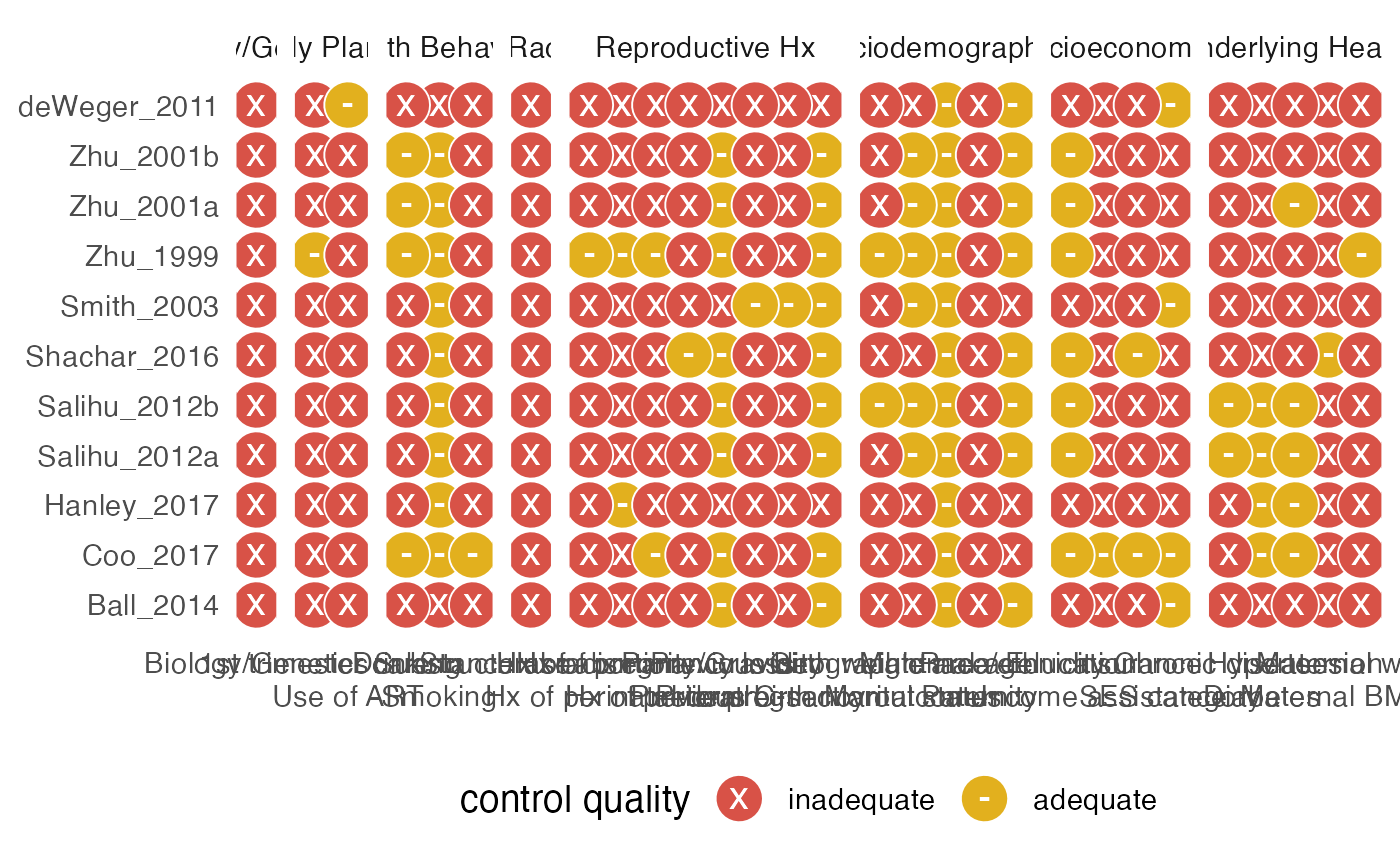
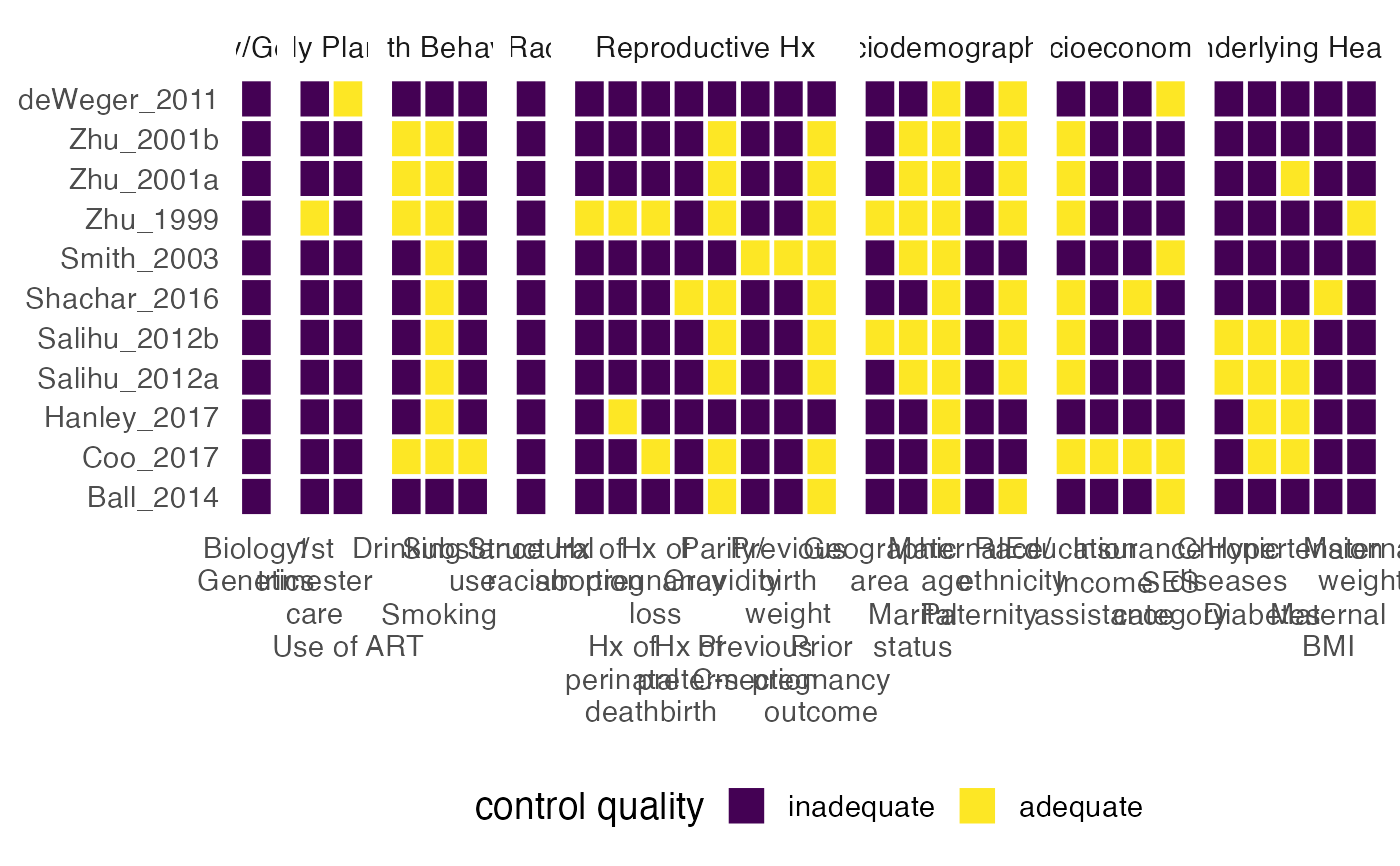
mc_heatmap() and mc_trafficlight() visualize the results of
metaconfoundr(), summarizing the quality of confounder control in each
study.
mc_heatmap(
.df,
legend_title = "control quality",
sort = FALSE,
by_group = FALSE,
score = c("adequate", "sum", "controlled"),
non_confounders = FALSE
)
mc_trafficlight(
.df,
size = 8,
legend_title = "control quality",
sort = FALSE,
by_group = FALSE,
score = c("adequate", "sum", "controlled"),
non_confounders = FALSE
)Arguments
- .df
A data frame, usually the result of
metaconfoundr()- legend_title
The legend title
- sort
Logical. Sort by confounder score? Calculated by
score_control()- by_group
Logical. If sorted, sort within domain?
- score
The approach used to calculate the score.
adequatetests if the study controlled at a strictly adequate level.sumtreatscontrol_qualityas an ordinal integer, summing it's values such that a higher score has better control overall.controlledtests if any control, includingsome concernscontrol, is present.- non_confounders
Logical. Include non-confounders? Default is
FALSE.- size
The size of the points in the traffic light plot
Value
a ggplot
See also
Other plots:
facet_constructs(),
geom_cochrane(),
scale_fill_cochrane(),
theme_mc()
Examples
ipi %>%
metaconfoundr() %>%
dplyr::mutate(variable = stringr::str_wrap(variable, 10)) %>%
mc_heatmap() +
theme_mc() +
facet_constructs() +
ggplot2::guides(x = ggplot2::guide_axis(n.dodge = 2))
 ipi %>%
metaconfoundr() %>%
mc_trafficlight() +
geom_cochrane() +
facet_constructs() +
scale_fill_cochrane() +
theme_mc() +
ggplot2::guides(x = ggplot2::guide_axis(n.dodge = 2))
ipi %>%
metaconfoundr() %>%
mc_trafficlight() +
geom_cochrane() +
facet_constructs() +
scale_fill_cochrane() +
theme_mc() +
ggplot2::guides(x = ggplot2::guide_axis(n.dodge = 2))